Agent Configuration
The SipPulse AI platform offers a comprehensive set of features to customize your Agents. The configuration interface mirrors the three main groups you see in the sidebar:
| Section | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Configuration | Core identity, behavior, voice, and call handling |
| Tools | Extend your agent with external capabilities |
| Advanced | Post-conversation analysis and insights |
Choosing the Right Channel
Not sure whether to deploy a voice or chat agent? See our Voice vs Chat comparison guide for best practices on when to use each modality.
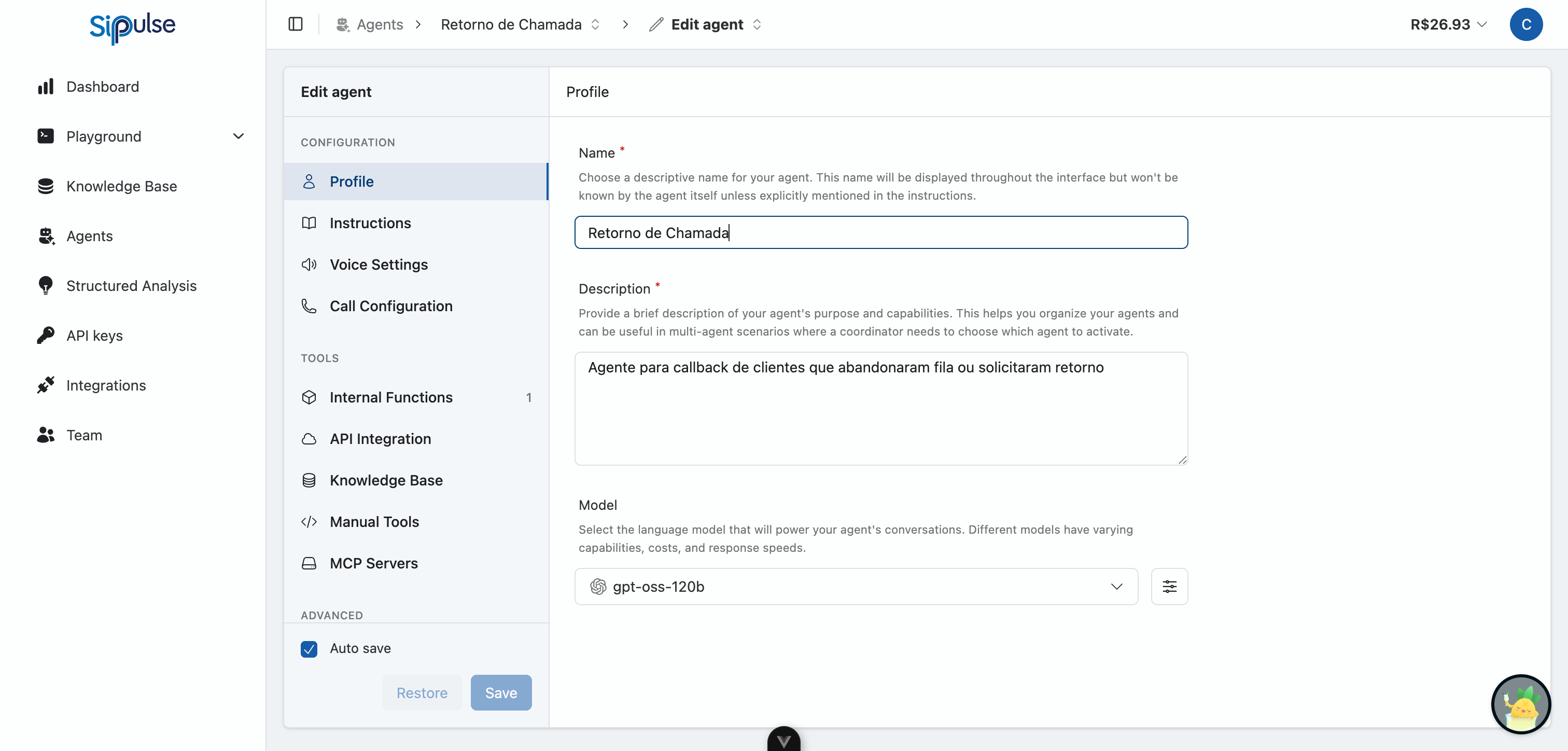
Configuration
The Configuration section defines your agent's core identity and behavior:
| Tab | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Profile | Agent name, description, and AI model selection |
| Instructions | Define personality, behavior, and knowledge domain |
| Voice Settings | Language, TTS provider, and voice selection |
| Call Configuration | Greeting, timeouts, and voice-specific tools |
Tools
Tools give your agent "superpowers" beyond conversation. Without tools, an agent can only chat—with tools, it can take actions in the real world.
| Tool Type | Best For |
|---|---|
| Built-in Functions | Calculator, current date/time |
| API Integration | REST API calls to external services |
| Knowledge Base | Document search (RAG) |
| Manual Tools | Custom logic in your backend |
| MCP Servers | Model Context Protocol integrations |
Tool Selection Strategy
Start with the simplest tool that solves your problem:
- Built-in for basic calculations and time
- Knowledge Base for answering questions from documents
- API Integration for standard REST endpoints
- MCP Servers for complex integrations with standardized protocol
- Manual Tools when you need full control over the logic
Advanced
Post Analysis
Automatically analyze conversations after they end:
- Customer satisfaction scoring
- Conversation summarization
- Intent classification
- Quality assurance metrics
Auto Save
The configuration interface includes an Auto save toggle in the bottom left. When enabled:
- Changes are automatically saved as you make them
- No need to manually click "Save"
When disabled:
- Use the Save button to apply changes
- Use Restore to revert to the last saved state
When to Disable Auto Save
Disable auto save when making experimental changes you might want to discard, or when you want to review all changes before applying them.
