Advanced Text Generation with Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models (LLMs) are sophisticated neural networks trained on vast amounts of textual data. This architecture allows them to generate coherent, contextually relevant, and creative responses from textual instructions (prompts). On the SipPulse AI platform, we offer access to a diverse selection of LLMs from leading global developers such as OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, Meta, Qwen, Deepseek, among others. Each model has distinct characteristics in terms of performance, cost, and specialization.
For a complete overview of all models, their detailed technical specifications, and the pricing structure, please refer to our official Pricing page.
Interactive Playground
The Text Generation Playground (access here) is a user-friendly web interface designed to facilitate experimentation and evaluation of each LLM's behavior.
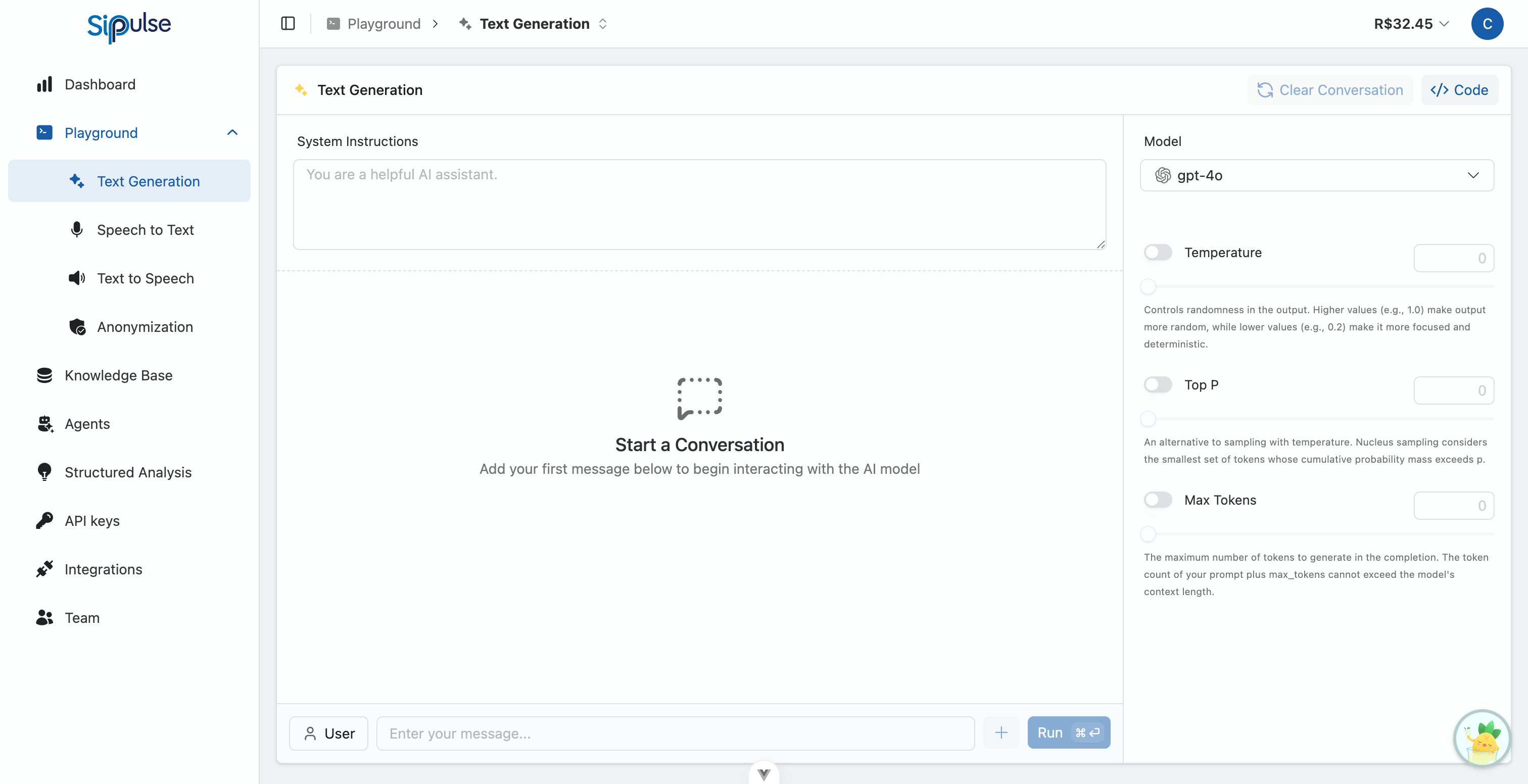
Model Selection
- Browse and choose any LLM listed in the selector.
Parameter Configuration
- Control parameters such as
temperature,max_tokens,top_p, and others. See the Parameter Guide for details. - Important: Each model supports different parameters. The Playground automatically displays only the relevant controls for the selected model.
Dynamic Parameters by Model
Reasoning models (like GPT-5, o1) use special parameters like reasoning_effort instead of temperature. Traditional models (GPT-4o, Claude) use temperature, top_p, max_tokens. Select a model in the Playground to see its available parameters.
Prompt and Message Creation
- Define a System Message to instruct the LLM on the tone, style, persona, or specific rules it should follow in its responses.
- Insert a sequence of user and assistant messages to simulate complex conversations and test the model's ability to maintain context.
- To learn how to create effective prompts and system messages, consult our Prompt Engineering Guide for LLMs.
Execution and Visualization
- Get instant feedback. The model's responses are displayed immediately after each prompt submission.
Code Generation
- With a click on "View Code", the Playground automatically generates code snippets in cURL, Python, and JavaScript.
- These examples include the exact model and parameters you configured, ready to be copied and pasted into your projects.
- Easily select the desired language using the tabs at the top of the code modal.
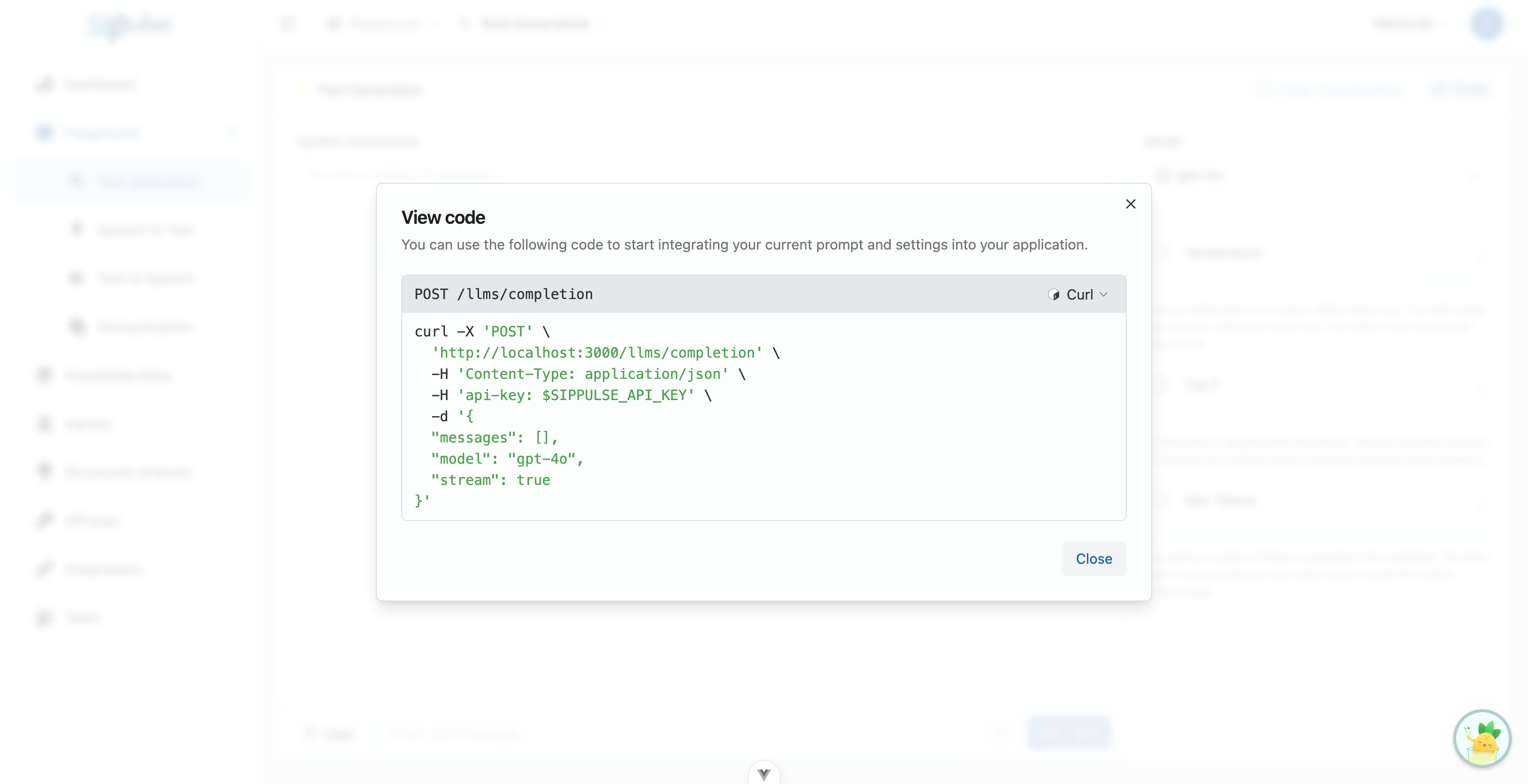
The Playground is a valuable tool for both users without programming experience who want to understand the potential of LLMs, and for experienced developers looking to quickly validate different configurations and models before implementation.
Keyboard Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
Cmd/Ctrl + Enter | Send message |
Shift + Enter | New line (without sending) |
Conversation Management
The Playground offers controls for managing your test conversation:
- Edit messages: Click the pencil icon to edit any sent message
- Toggle role: Switch between "user" and "assistant" to simulate different scenarios
- Clear conversation: Use the "Clear" button to restart the conversation
- Multiple messages: Add multiple messages before running to test complex contexts
Model Information
The selected model card displays useful information:
- Context window: Maximum context size in tokens
- Pricing: Cost per million tokens (input/output)
- "Agent" badge: Indicates the model supports tool calling
Consumption via REST API
Integrate the power of LLMs directly into your applications, custom scripts, and automated workflows through calls to our RESTful endpoint.
For details, see How to use the API.
# Example request to complete a text
# Replace $SIPPULSE_API_KEY with your API key.
curl -X POST 'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'api-key: $SIPPULSE_API_KEY' \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are an AI assistant specialized in space history." },
{ "role": "user", "content": "Describe in detail the importance of the Apollo 11 mission." }
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 250,
"stream": false # Set to true to receive the response in parts (streaming)
}'import os
import requests
import json
def generate_text_completion(messages: list, model: str = "gpt-4o-mini", temperature: float = 0.7, max_tokens: int = 250, stream: bool = False) -> dict:
"""
Calls the /v1/llms/completion endpoint to generate text with an LLM.
Args:
messages: List of messages (conversation history).
model: Model identifier to be used.
temperature: Controls the randomness of the output.
max_tokens: Maximum number of tokens to be generated.
stream: If true, the response will be sent in parts.
Returns:
Dictionary containing the API response.
"""
api_url = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion"
api_key = os.getenv("SIPPULSE_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
raise ValueError("The SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not defined.")
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"api-key": api_key
}
payload = {
"model": model,
"messages": messages,
"temperature": temperature,
"max_tokens": max_tokens,
"stream": stream
}
try:
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
response.raise_for_status() # Raises an exception for error responses (4xx or 5xx)
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"API request error: {e}")
if response is not None:
print(f"Error details: {response.text}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
convo_messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI assistant specialized in space history."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Describe in detail the importance of the Apollo 11 mission."}
]
completion_result = generate_text_completion(convo_messages, model="gpt-4o-mini")
if completion_result:
# The response structure may vary depending on the model and if stream=true
# Generally, the generated content is in completion_result['choices'][0]['message']['content']
print(json.dumps(completion_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))// Example using the Fetch API in Node.js or browser
async function getTextCompletion(messages, model = "gpt-4o-mini", temperature = 0.7, maxTokens = 250, stream = false) {
const apiUrl = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion";
const apiKey = process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY; // Make sure SIPPULSE_API_KEY is in the environment
if (!apiKey) {
throw new Error("The SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not defined.");
}
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"api-key": apiKey
},
body: JSON.stringify({
model,
messages,
temperature,
max_tokens: maxTokens,
stream
})
});
if (!response.ok) {
const errorBody = await response.text();
throw new Error(`API Error: ${response.status} ${response.statusText} - ${errorBody}`);
}
return response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to call the completion API:", error);
throw error;
}
}
// Usage example
const conversationMessages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are an AI assistant specialized in space history." },
{ role: "user", content: "Describe in detail the importance of the Apollo 11 mission." }
];
getTextCompletion(conversationMessages)
.then(result => console.log(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)))
.catch(error => console.error(error));Response Structure
The API returns an object with the generated response, usage information, and performance metrics:
{
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "The Apollo 11 mission was a historic milestone..."
},
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"created": 1704067200000,
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"usage": {
"input_tokens": 45,
"output_tokens": 120,
"total_tokens": 165
},
"performance": {
"delay": 150,
"execution_time": 1200,
"relative_execution_time": 100.0
}
}| Field | Description |
|---|---|
choices | Array of responses generated by the model |
choices[].message | Assistant message with role and content |
choices[].finish_reason | Termination reason: stop, length, tool_calls |
usage.input_tokens | Tokens consumed by the input prompt |
usage.output_tokens | Tokens generated in the response |
performance.execution_time | Execution time in milliseconds |
Streaming Responses
For real-time responses as they are generated, set stream: true. The API returns chunks in Server-Sent Events (SSE) format, ideal for chat interfaces.
When to Use Streaming
| Scenario | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Interactive chat | ✅ Use streaming |
| Batch processing | ❌ Don't use |
| Long responses | ✅ Use streaming |
| Simple integration | ❌ Don't use |
Chunk Format
Each chunk follows the SSE format:
data: {"choices":[{"delta":{"content":"text"}}]}
data: {"choices":[{"delta":{"content":" partial"}}]}
data: [DONE]| Field | Description |
|---|---|
delta.content | Generated text fragment |
delta.role | Present only in the first chunk |
delta.tool_calls | Present when there are tool calls in streaming |
Complete Examples
async function streamCompletion(messages) {
const response = await fetch('https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'api-key': process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY
},
body: JSON.stringify({
model: 'gpt-4o-mini',
messages,
stream: true
})
});
const reader = response.body.getReader();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
let fullContent = '';
while (true) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) break;
const chunk = decoder.decode(value);
const lines = chunk.split('\n');
for (const line of lines) {
if (line.startsWith('data: ') && line !== 'data: [DONE]') {
try {
const data = JSON.parse(line.slice(6));
const content = data.choices[0]?.delta?.content || '';
fullContent += content;
process.stdout.write(content); // Display in real-time
} catch (e) {
// Ignore malformed lines
}
}
}
}
return fullContent;
}import requests
import json
import os
def stream_completion(messages):
response = requests.post(
'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion',
headers={
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'api-key': os.environ['SIPPULSE_API_KEY']
},
json={
'model': 'gpt-4o-mini',
'messages': messages,
'stream': True
},
stream=True
)
full_content = ''
for line in response.iter_lines():
if line:
line_text = line.decode('utf-8')
if line_text.startswith('data: ') and line_text != 'data: [DONE]':
try:
data = json.loads(line_text[6:])
content = data['choices'][0]['delta'].get('content', '')
full_content += content
print(content, end='', flush=True)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
pass
return full_contentStreaming with Tool Calls
In streaming mode, tool calls are sent incrementally:
data: {"choices":[{"delta":{"tool_calls":[{"index":0,"id":"call_abc","function":{"name":"get_weather"}}]}}]}
data: {"choices":[{"delta":{"tool_calls":[{"index":0,"function":{"arguments":"{\"ci"}}]}}]}
data: {"choices":[{"delta":{"tool_calls":[{"index":0,"function":{"arguments":"ty\": \"NYC\"}"}}]}}]}
data: [DONE]You must accumulate the arguments fragments until you receive [DONE].
Final Chunk with Token Usage
The last chunk before [DONE] includes usage information:
{
"choices": [{"delta": {}, "finish_reason": "stop"}],
"usage": {
"input_tokens": 45,
"output_tokens": 120
}
}Tool Calling (Function Calling)
Models with the capability tools: true support tool calling, allowing the model to request execution of external functions and use the results to generate responses.
Check Compatibility
Verify if the model supports tools by checking the resources array in the /v1/llms/models response. If resources contains "tools", the model supports tool calling.
Defining Tools
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [
{ "role": "user", "content": "What's the weather forecast in New York?" }
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Gets the weather forecast for a city",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "City name"
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
}
]
}Response with Tool Call
When the model decides to use a tool, the response includes tool_calls:
{
"choices": [{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [{
"id": "call_abc123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\": \"New York\"}"
}
}]
},
"finish_reason": "tool_calls"
}]
}Sending Tool Result
After executing the tool in your system, send the result back:
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [
{ "role": "user", "content": "What's the weather forecast in New York?" },
{
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": [{
"id": "call_abc123",
"type": "function",
"function": { "name": "get_weather", "arguments": "{\"city\": \"New York\"}" }
}]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": "call_abc123",
"content": "{\"temperature\": 72, \"condition\": \"sunny\", \"humidity\": 45}"
}
]
}The model then generates a response using the tool data:
{
"choices": [{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "In New York, the temperature is 72°F with sunny skies and 45% humidity."
},
"finish_reason": "stop"
}]
}Error Handling
HTTP Codes
| Code | Error | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | bad_request | Malformed request or invalid parameters |
| 401 | unauthorized | Invalid or missing API key |
| 404 | model_not_found | Model doesn't exist or is unavailable |
| 429 | rate_limit_exceeded | Request limit exceeded |
| 500 | internal_error | Internal server error |
| 503 | service_unavailable | Service temporarily unavailable |
| 504 | timeout | Timeout exceeded |
Error Structure
{
"error": {
"code": "model_not_found",
"message": "The model 'gpt-99' does not exist or is not available for your organization."
}
}Common Errors and Solutions
| Code | Common Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
invalid_api_key | Incorrect API key | Check your key in Settings > API Keys |
model_does_not_support_json_schema | Model incompatible with structured output | Use a model with structured_output: true |
context_length_exceeded | Prompt too long | Reduce message size or use a model with larger context |
rate_limit_exceeded | Too many requests | Wait or integrate your own API key |
Integrate Your Own API Key
If you frequently hit rate limits, consider integrating your own API key from providers like OpenAI or Anthropic. This allows you to use your own limits and direct billing.
Error Handling Example
try {
const response = await fetch('https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'api-key': apiKey },
body: JSON.stringify({ model, messages })
});
if (!response.ok) {
const error = await response.json();
switch (error.error?.code) {
case 'rate_limit_exceeded':
// Implement retry with backoff
await sleep(5000);
return retry();
case 'context_length_exceeded':
// Truncate messages
return retryWithShorterContext();
default:
throw new Error(error.error?.message || 'Unknown error');
}
}
return response.json();
} catch (e) {
console.error('API Error:', e.message);
}import time
def call_with_retry(messages, max_retries=3):
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
response = requests.post(
'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/completion',
headers={'api-key': api_key, 'Content-Type': 'application/json'},
json={'model': 'gpt-4o-mini', 'messages': messages}
)
if response.status_code == 429:
# Rate limited - wait and retry
time.sleep(2 ** attempt)
continue
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
raise
time.sleep(2 ** attempt)Available Models
To keep your application up-to-date with the LLMs enabled for your organization, use the /v1/llms/models endpoint. This allows your application to dynamically adapt to available models without requiring manual code updates.
# Lists all LLM models available for your API key
curl -X GET 'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/models' \
-H 'api-key: $SIPPULSE_API_KEY'import os
import requests
import json
def list_available_models() -> dict:
"""
Retrieves the list of LLMs available for the organization associated with the API key.
"""
api_url = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/models"
api_key = os.getenv("SIPPULSE_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
raise ValueError("The SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not defined.")
headers = { "api-key": api_key }
try:
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"API request error for listing models: {e}")
if response is not None:
print(f"Error details: {response.text}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
models_data = list_available_models()
if models_data:
print("Available Models:")
print(json.dumps(models_data, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))// Example using the Fetch API to list models
async function listAvailableModels() {
const apiUrl = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/llms/models";
const apiKey = process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY;
if (!apiKey) {
throw new Error("The SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not defined.");
}
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: "GET",
headers: { "api-key": apiKey }
});
if (!response.ok) {
const errorBody = await response.text();
throw new Error(`API error when listing models: ${response.status} ${response.statusText} - ${errorBody}`);
}
return response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to call the API to list models:", error);
throw error;
}
}
listAvailableModels()
.then(models => console.log("Available Models:", JSON.stringify(models, null, 2)))
.catch(error => console.error(error));Response Example
[
{
"name": "gpt-4o",
"status": "active",
"execution_type": "cloud",
"resources": ["tools", "json_schema"]
},
{
"name": "gpt-4o-mini",
"status": "active",
"execution_type": "cloud",
"resources": ["tools", "json_schema"]
},
{
"name": "claude-sonnet-4-20250514",
"status": "active",
"execution_type": "cloud",
"resources": ["tools", "json_schema"]
}
]| Field | Description |
|---|---|
name | Model identifier for API usage |
status | Model status: active, inactive, deprecated |
execution_type | Execution type (always cloud) |
resources | Array of capabilities: tools, json_schema |
Resources Field
The resources field indicates capabilities supported by the model:
"tools"- Supports tool calling (function calling)"json_schema"- Supports structured output with JSON Schema
For detailed model information (context window, pricing, parameters), see the Pricing page.
OpenAI SDK
For developers familiar with the official OpenAI SDK, SipPulse AI offers a simplified integration. Simply configure the baseURL of the OpenAI client to point to our compatible endpoint: https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/openai.
This allows you to utilize all the functionalities and conventions of the OpenAI SDK, while the requests are processed by the SipPulse AI infrastructure, leveraging our selection of models and optimizations.
# Example usage with the OpenAI Python SDK
import os
from openai import OpenAI
# Configure the OpenAI client to use the SipPulse AI endpoint
client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.environ.get("SIPPULSE_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/openai"
)
try:
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini", # Or any other compatible model available on SipPulse AI
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant who loves puns."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me a joke about programming."}
],
temperature=0.6,
max_tokens=100
)
print(chat_completion.choices[0].message.content)
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")// Example usage with the OpenAI JavaScript SDK
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY, // Your SipPulse AI key
baseURL: "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/openai" // SipPulse AI compatible endpoint
});
async function main() {
try {
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini", // Or any other compatible model
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant who loves puns." },
{ role: "user", content: "Tell me a joke about programming." }
],
temperature: 0.6,
max_tokens: 100
});
console.log(response.choices[0].message.content);
} catch (error) {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
}
}
main();Benefit: This approach allows you to maintain the familiarity and conveniences of the OpenAI SDK, such as typing and specific methods, while your calls are routed and executed through the SipPulse AI platform. You can switch between OpenAI models and other models offered by SipPulse AI, if supported by the compatibility endpoint.
Parameter Guide
Generation parameters vary according to the selected model. The Playground automatically displays only the relevant controls for the chosen model.
Parameters by Model Type
- Reasoning models (GPT-5, o1): use
reasoning_effortinstead oftemperature - Traditional models (GPT-4o, Claude): use
temperature,top_p,max_tokens
Common Parameters
| Parameter | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
temperature | 0-2 | Controls randomness. Low = focused, high = creative |
max_tokens | 1-128k | Maximum token limit in the response |
top_p | 0-1 | Nucleus sampling. Alternative to temperature |
top_k | 1-100 | Limits selection to the K most probable tokens |
frequency_penalty | -2 to 2 | Penalizes token repetition |
presence_penalty | -2 to 2 | Encourages new topics |
Usage Tips
- Precise tasks (code, extraction): use low
temperature(0.0-0.3) - Creative tasks (writing, brainstorming): use higher
temperature(0.7-1.0) - Adjust
temperatureortop_p, not both at the same time - Total
max_tokens(prompt + response) cannot exceed the model's limit
The best way to understand these parameters is to experiment in the Playground.
