Text-to-Speech (TTS)
TTS (Text-to-Speech) services from SipPulse AI convert written text into natural-sounding audio, enabling your applications to "speak" to users. Our platform offers a variety of models from renowned providers such as OpenAI, ElevenLabs, and Microsoft, each with a distinct set of voices and features.
For detailed information on pricing and model specifications, see our Pricing page.
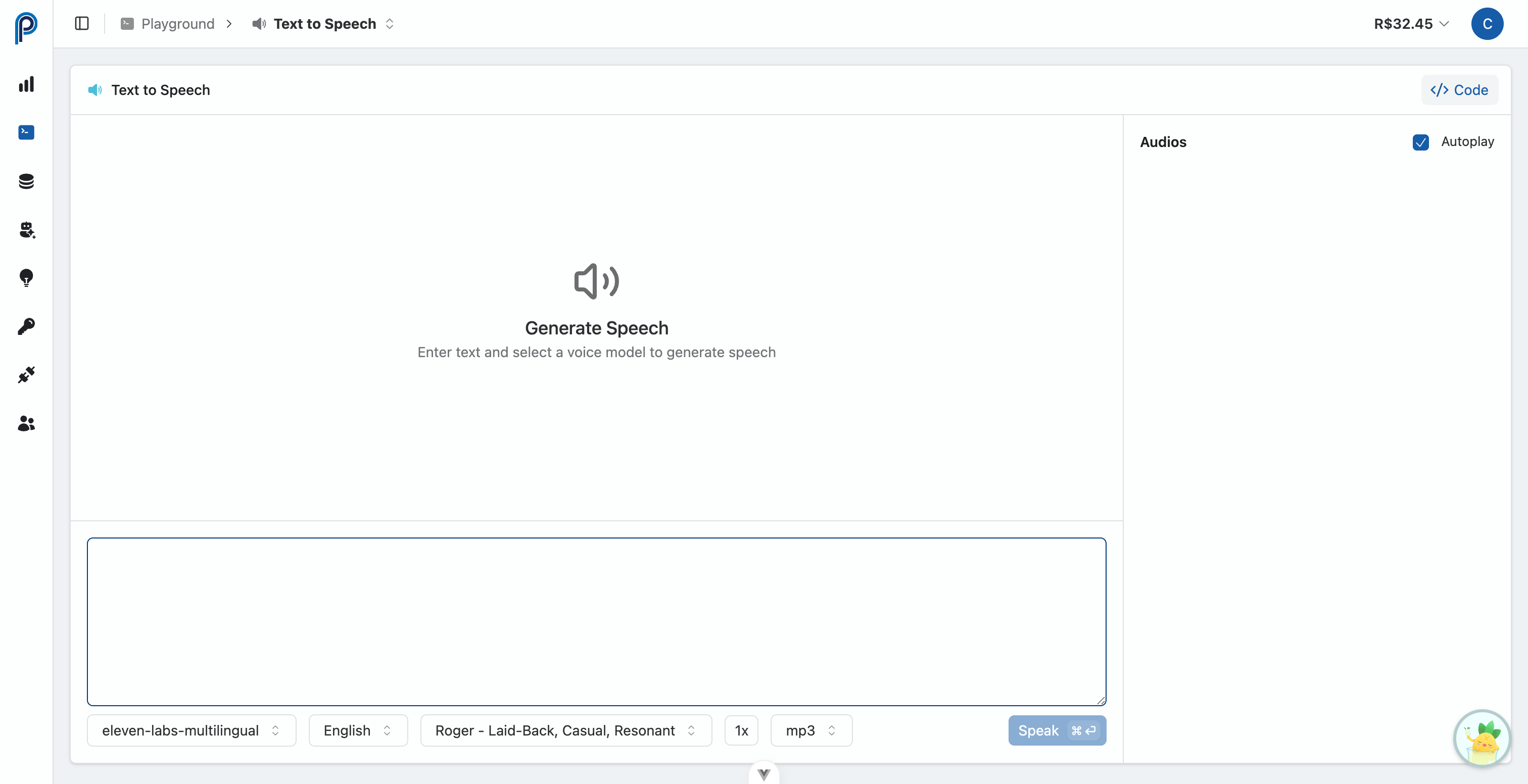
1. Interactive Text-to-Speech Playground
The Interactive Text-to-Speech Playground (access here) is the ideal tool to experiment with and validate TTS models intuitively before integrating them via API:
- Model and Voice Selection: Explore various speech synthesis models (OpenAI, ElevenLabs, Microsoft) and the available voices for each.
- Text Input: Enter the text you want to convert to audio.
- Parameter Adjustment: Configure parameters such as speed (
speed) and audio output format (response_format). - Immediate Generation and Playback: Run the synthesis and listen to the resulting audio directly in the interface.
- Code Preview: Get code samples in cURL, Python, and JavaScript, pre-configured with the model, voice, and parameters you tested, making implementation easier.
The Playground is an excellent way to discover the perfect voice for your project and understand how different parameters affect the final speech synthesis result.
2. Consuming via REST API
Integrating TTS functionality into your applications is done through calls to our REST API.
2.1. Synthesize Speech
Use the /v1/tts/generate endpoint to convert a text string into audio data.
Endpoint: POST /v1/tts/generate
Request Body (JSON):
input(string, required): The text to be converted to speech.model(string, required): The TTS model name to use (e.g.,"tts-1"for OpenAI,"eleven_multilingual_v2"for ElevenLabs, or a specific Microsoft model). See the/v1/tts/modelsendpoint for a list of available models.voice(string, required): The key of the specific voice to use for synthesis (e.g.,"alloy","shimmer"for OpenAI TTS; a voice ID for ElevenLabs; or a Microsoft voice name like"pt-BR-FranciscaNeural"). See the/v1/tts/voicesendpoint for available voice keys for each model.response_format(string, optional, default:"mp3"): The output audio file format. Supported values:"mp3","opus","aac","flac","wav","pcm".speed(float, optional, default:1.0): Controls speech speed. Typical values between0.25and4.0. The exact range may vary by model.
Dynamic Parameters
The available parameters vary by model. Use the Playground to see which parameters are supported for each model. Common parameters include speed and response_format, but not all models support all options.
Response (JSON):
- Success (200 OK):
{
"filename": "string", // Generated file name
"usage": {}, // Usage info (may vary)
"performance": {}, // Performance info (may vary)
"unit": "string", // Cost unit (e.g., "characters")
"stream": "string", // URL for audio streaming
"download": "string" // URL for audio download
}- Error: JSON response with appropriate HTTP status code and error details in the body.
# Example: Synthesize speech
curl -X POST 'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/generate' \
-H 'api-key: $SIPPULSE_API_KEY' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"input": "Hello, world! This is a speech synthesis demo.",
"model": "tts-1",
"voice": "alloy",
"response_format": "mp3",
"speed": 1.1
}'import os
import requests
import json
def synthesize_speech(
text_input: str,
model_id: str,
voice_key: str,
response_format: str = "mp3",
speed: float = 1.0
) -> dict | None:
"""
Synthesizes speech from text using the SipPulse AI API.
"""
api_url = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/generate"
api_key = os.getenv("SIPPULSE_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
print("Error: SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not set.")
return None
headers = {
"api-key": api_key,
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"input": text_input,
"model": model_id,
"voice": voice_key,
"response_format": response_format,
"speed": speed
}
try:
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(payload))
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
error_content = e.response.text
try:
error_json = e.response.json()
error_content = json.dumps(error_json, indent=2)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
pass
print(f"API error: {e.response.status_code}\n{error_content}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
tts_result = synthesize_speech(
text_input="Testing speech synthesis with the API.",
model_id="tts-1", # Example with OpenAI model
voice_key="nova", # Example with OpenAI voice
response_format="mp3",
speed=1.0
)
if tts_result:
print("Synthesis successful:")
print(json.dumps(tts_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
print(f"Download link: {tts_result.get('download')}")
print(f"Stream link: {tts_result.get('stream')}")// Node.js with fetch
async function synthesizeSpeech({
textInput,
modelId,
voiceKey,
responseFormat = "mp3",
speed = 1.0,
}) {
const apiUrl = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/generate";
const apiKey = process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY;
if (!apiKey) {
console.error("SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not set.");
return null;
}
const payload = {
input: textInput,
model: modelId,
voice: voiceKey,
response_format: responseFormat,
speed,
};
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"api-key": apiKey,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(payload),
});
if (!response.ok) {
let errorBody = await response.text();
try {
errorBody = JSON.stringify(JSON.parse(errorBody), null, 2);
} catch (e) { /* not JSON */ }
throw new Error(`API error: ${response.status} ${response.statusText}\n${errorBody}`);
}
return response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to synthesize speech:", error);
return null;
}
}
// Usage example:
// (async () => {
// const result = await synthesizeSpeech({
// textInput: "Hello, JavaScript speaking here!",
// modelId: "eleven_multilingual_v2", // Example with ElevenLabs
// voiceKey: "VOICE_ID_ELEVENLABS", // Replace with desired ElevenLabs voice ID
// responseFormat: "opus",
// speed: 0.9
// });
// if (result) {
// console.log("Synthesis result:", JSON.stringify(result, null, 2));
// }
// })();2.2. List Available TTS Models
To query the TTS (Text-to-Speech) models currently available for your organization:
Endpoint: GET /v1/tts/models
Query Parameters:
status(string, optional): Filter models by status (activeorinactive). Default:active.
curl -X GET 'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/models?status=active' \
-H 'api-key: $SIPPULSE_API_KEY' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'import os
import requests
def list_tts_models(status: str = "active") -> list | None:
"""
Lists available TTS models from the SipPulse AI API.
"""
api_url = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/models"
api_key = os.getenv("SIPPULSE_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
print("Error: SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not set.")
return None
headers = {
"api-key": api_key,
"Accept": "application/json"
}
params = {"status": status}
try:
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers, params=params)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
print(f"API error: {e.response.status_code}")
return None
# Usage
models = list_tts_models()
if models:
for model in models:
print(f"{model['name']} ({model['provider']})")async function listTTSModels(status = "active") {
const apiUrl = `https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/models?status=${status}`;
const apiKey = process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY;
if (!apiKey) {
console.error("SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not set.");
return null;
}
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"api-key": apiKey,
"Accept": "application/json",
},
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`API error: ${response.status}`);
}
return response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to list TTS models:", error);
return null;
}
}
// Usage
// const models = await listTTSModels();
// models?.forEach(m => console.log(`${m.name} (${m.provider})`));Example Response (JSON):
[
{
"name": "tts-1",
"status": "active",
"provider": "openai"
},
{
"name": "eleven_multilingual_v2",
"status": "active",
"provider": "elevenlabs"
},
{
"name": "azure-tts",
"status": "active",
"provider": "microsoft"
}
]2.3. List Available Voices
To query the voices available for synthesis. The response is a Record where the key is the model name and the value is a list of its voices.
Endpoint: GET /v1/tts/voices
curl -X GET 'https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/voices' \
-H 'api-key: $SIPPULSE_API_KEY' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'import os
import requests
def list_tts_voices(model: str = None) -> dict | None:
"""
Lists available voices for TTS models.
Optionally filter by model name.
"""
api_url = "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/voices"
api_key = os.getenv("SIPPULSE_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
print("Error: SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not set.")
return None
headers = {
"api-key": api_key,
"Accept": "application/json"
}
params = {"model": model} if model else {}
try:
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers, params=params)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
print(f"API error: {e.response.status_code}")
return None
# Usage
voices = list_tts_voices()
if voices:
for model_name, voice_list in voices.items():
print(f"\n{model_name}:")
for voice in voice_list[:3]: # Show first 3 voices
print(f" - {voice['name']} ({voice['key']}) - {voice['languages']}")async function listTTSVoices(model = null) {
const params = model ? `?model=${model}` : "";
const apiUrl = `https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/tts/voices${params}`;
const apiKey = process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY;
if (!apiKey) {
console.error("SIPPULSE_API_KEY environment variable is not set.");
return null;
}
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"api-key": apiKey,
"Accept": "application/json",
},
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`API error: ${response.status}`);
}
return response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to list TTS voices:", error);
return null;
}
}
// Usage
// const voices = await listTTSVoices("tts-1");
// Object.entries(voices).forEach(([model, voiceList]) => {
// console.log(`${model}: ${voiceList.length} voices`);
// });Example Response (JSON):
{
"tts-1": [
{ "name": "Alloy", "key": "alloy", "languages": ["multi"] },
{ "name": "Echo", "key": "echo", "languages": ["multi"] },
{ "name": "Nova", "key": "nova", "languages": ["multi"] }
],
"eleven_multilingual_v2": [
{ "name": "Rachel", "key": "21m00Tcm4TlvDq8ikWAM", "languages": ["multi"] },
{ "name": "Adam", "key": "pNInz6obpgDQGcFmaJgB", "languages": ["multi"] }
],
"azure-tts": [
{ "name": "Francisca", "key": "pt-BR-FranciscaNeural", "languages": ["pt-BR"] },
{ "name": "Emma", "key": "en-US-EmmaNeural", "languages": ["en-US"] }
]
}Use the desired voice
keyin thevoiceparameter of the synthesis request (/v1/tts/generate).
3. Supported Audio Formats (response_format)
SipPulse AI TTS supports the following audio output formats:
| Format | MIME Type | Size | Quality | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
mp3 | audio/mpeg | Small | Good | Web applications, general use |
opus | audio/ogg | Very small | Excellent | Real-time streaming, VoIP |
aac | audio/aac | Small | Very good | Mobile apps, iOS |
flac | audio/flac | Large | Lossless | Archival, professional audio |
wav | audio/wav | Very large | Lossless | Audio editing, processing |
pcm | audio/L16 | Very large | Raw | Telephony systems, custom processing |
Format Recommendations
- Web applications: Use
mp3for broad compatibility - Real-time/streaming: Use
opusfor best compression - Mobile apps: Use
aacfor iOS oropusfor Android - Telephony/IVR: Use
pcm(24kHz mono) for direct integration
Choose the format that best fits your application's requirements in terms of quality, file size, and audio player compatibility.
4. Integration with OpenAI SDK
For developers who prefer to use the official OpenAI SDK, SipPulse AI offers compatibility. Set the OpenAI client's baseURL to the SipPulse AI endpoint: https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/openai.
When using this integration for TTS, the SipPulse AI API will return the binary audio stream in the requested format, instead of a JSON object with download/stream links. This matches the default behavior of the OpenAI SDK for speech synthesis.
The OpenAI SDK compatibility endpoint supports the standard parameters defined by the OpenAI API. Parameter availability may vary depending on the specific model.
import os
from openai import OpenAI
# Configure the OpenAI client to use the SipPulse AI endpoint
client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.environ.get("SIPPULSE_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/openai" # SipPulse AI compatibility endpoint
)
try:
response = client.audio.speech.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="alloy",
input="Hello, this audio was generated using the OpenAI SDK via SipPulse AI!",
response_format="mp3",
speed=1.0 # Optional: 0.25 to 4.0
)
# The 'response' contains the audio stream.
# You can save it to a file:
response.stream_to_file("sippulse_openai_sdk_output.mp3")
print("Audio generated and saved as sippulse_openai_sdk_output.mp3")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")// Example usage with the OpenAI JavaScript SDK in Node.js
import OpenAI from "openai";
import fs from "fs";
import path from "path";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.SIPPULSE_API_KEY,
baseURL: "https://api.sippulse.ai/v1/openai"
});
async function main() {
try {
const speechStream = await openai.audio.speech.create({
model: "tts-1",
voice: "nova",
input: "Testing speech synthesis with the JavaScript SDK and SipPulse AI.",
response_format: "opus"
});
// speechStream is a ReadableStream. You can save it to a file.
const filePath = path.resolve("./sippulse_openai_sdk_output.opus");
const writer = fs.createWriteStream(filePath);
// Node.js < 18 (without ReadableStream.toWeb()):
// speechStream.body.pipe(writer);
// await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// writer.on("finish", resolve);
// writer.on("error", reject);
// });
// Node.js >= 18 (with ReadableStream.toWeb() and Readable.fromWeb())
// Or if the SDK returns a Node ReadableStream directly:
for await (const chunk of speechStream) {
writer.write(chunk);
}
writer.end();
// Alternatively, if speechStream.body is a web stream:
// const nodeStream = Readable.fromWeb(speechStream.body);
// nodeStream.pipe(writer);
// ... (promise code to wait for 'finish')
console.log(`Audio generated and saved as ${filePath}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
}
}
main();Note: The OpenAI SDK compatibility endpoint supports OpenAI TTS models (
tts-1,tts-1-hd) with their standard voices. For access to other providers like ElevenLabs or Azure, use the native REST API (/v1/tts/generate).
5. Best Practices for Speech Synthesis
- Clear and Well-Structured Text: Provide grammatically correct and well-punctuated text for the best prosody and intelligibility.
- Appropriate Voice and Language Selection: Use the
/v1/tts/modelsand/v1/tts/voicesendpoints to select the model and voice combination that best fits your target audience and application context. - Experiment with Output Formats: Test different
response_formatvalues to find the ideal balance between sound quality and file size. - Robust Error Handling: Implement detailed error handling in your application to deal with possible API failures.
- Caching: For frequently synthesized texts, store the
downloadorstreamlinks (or the audio itself, if downloaded) to avoid repeated requests and optimize costs and latency.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How are costs calculated for the TTS service?
A: Costs are typically based on the number of characters in the input field processed for synthesis. Different models and voices (especially premium or custom ones) may have different costs. See the Pricing page and your account dashboard for precise details.
Q: Can I use the download and stream links multiple times?
A: Yes, the links provided in the /v1/tts/generate API response can be used to access the generated audio. However, the long-term availability of these links may depend on SipPulse AI's storage policies. For persistent use, it is recommended to download the audio.
