Instructions
The Instructions tab is the heart of your agent's configuration. Here you define who your agent is, how it should behave, and what it knows. Well-crafted instructions are the difference between a generic chatbot and a sophisticated AI assistant.
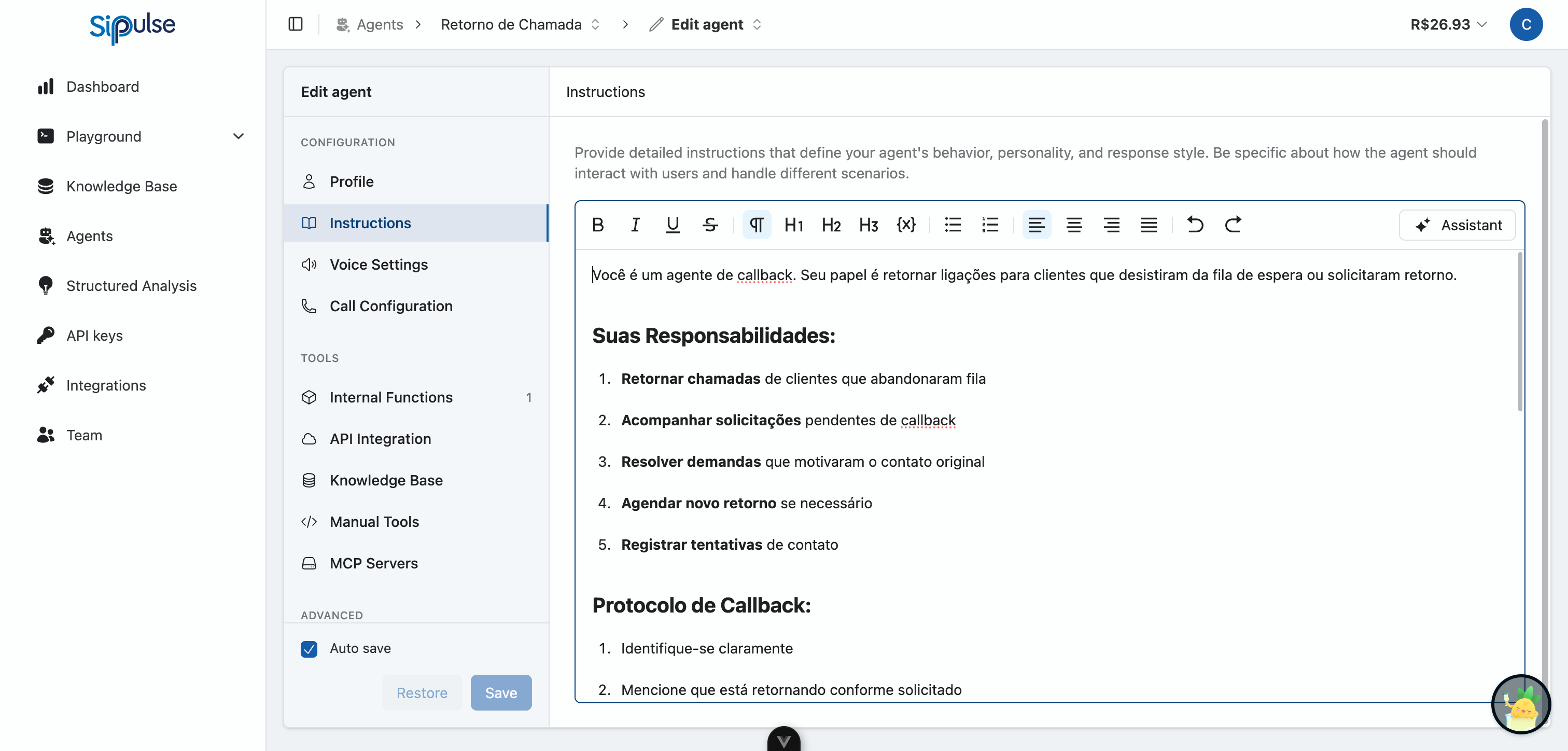
The Instruction Editor
The instructions editor provides a rich text environment for writing your agent's system prompt. This prompt is sent to the LLM at the beginning of every conversation, establishing the context for all interactions.
What to Include in Instructions
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | Who the agent is | "You are Sarah, a customer service specialist at TechCorp" |
| Personality | How it communicates | "Be friendly but professional, use simple language" |
| Knowledge Domain | What it knows about | "You specialize in our SaaS billing system" |
| Behavior Rules | What it should/shouldn't do | "Never discuss competitor products" |
| Conversation Flow | How to structure interactions | "Always confirm the issue before offering solutions" |
Instructions vs. Knowledge Base
Instructions define behavior—how your agent thinks and responds. Knowledge Base provides facts—specific information the agent can look up. Use instructions for personality and rules; use Knowledge Base for FAQs, documentation, and data.
Dynamic Variables
Dynamic variables let you personalize conversations by injecting runtime data into your instructions. Use the syntax {{variable_name}} in your instructions, and the values are replaced when a conversation thread is created.
How Variables Work
Variables are user-defined—you create any variables you need and pass their values when starting a conversation. There are no predefined variables; you have full flexibility.
In your instructions:
You are a support agent for {{company_name}}. The customer you're speaking
with is {{user_name}} (Account: {{account_id}}).
When greeting the customer, use their name: "Hello {{user_name}}, how can
I help you today?"When creating a thread via API:
{
"agentId": "agent-uuid",
"vars": {
"user_name": "John Smith",
"account_id": "ACC-12345",
"company_name": "Acme Corp"
}
}Variable Resolution
- Variables are replaced at thread creation time (not during the conversation)
- Values remain fixed for the entire conversation
- Unresolved variables appear as literal text (useful for debugging)
- You can use any variable names—they're not restricted to a predefined list
Prompt Writing Assistant
Click the Writing Assistant button to get AI-powered help crafting effective prompts. The assistant can:
- Improve existing instructions
- Suggest missing elements
- Optimize for specific use cases
- Fix common prompt engineering mistakes
When to Use the Assistant
The assistant is particularly helpful when:
- Starting from scratch and need a template
- Your agent isn't behaving as expected
- You want to optimize for a specific model
- You need to add structure to rambling instructions
Instruction Best Practices
1. Be Specific, Not Vague
❌ Vague:
"Be helpful and answer questions."
✅ Specific:
"Help customers troubleshoot billing issues. Start by confirming their account status, then walk through solutions step-by-step. If the issue requires manual intervention, collect the necessary details and escalate to the billing team."
2. Define Boundaries Clearly
Specify what your agent should NOT do:
## Limitations
- Do NOT provide legal or medical advice
- Do NOT process refunds directly—escalate to human support
- Do NOT discuss competitor products or pricing
- Do NOT share internal company information3. Structure with Markdown
Use headings, lists, and formatting to organize complex instructions:
# Role
You are Alex, a technical support specialist for CloudServices Inc.
# Personality
- Professional but approachable
- Patient with non-technical users
- Concise—avoid unnecessary explanations
# Knowledge Areas
1. Account management
2. API integration support
3. Billing inquiries
# Escalation Rules
Escalate to human support when:
- Customer requests a refund
- Technical issue persists after 3 troubleshooting attempts
- Customer explicitly asks for human assistance4. Include Example Interactions
Show your agent how to respond in specific scenarios:
## Example Interactions
**Scenario: Customer can't log in**
Customer: "I can't access my account"
Agent: "I'm sorry you're having trouble logging in. Let me help you with that.
First, could you tell me if you're seeing any specific error message when you
try to sign in?"
**Scenario: Pricing question**
Customer: "How much does the Pro plan cost?"
Agent: "Our Pro plan is $49/month when billed monthly, or $39/month when
billed annually. Would you like me to explain what's included in the Pro tier?"5. Handle Edge Cases
Anticipate unusual situations:
## Edge Cases
**Angry customers:**
Acknowledge their frustration first: "I completely understand how frustrating
this must be." Then focus on resolution.
**Off-topic requests:**
Politely redirect: "I specialize in billing support. For [their topic], I'd
recommend contacting our [appropriate team] at [contact info]."
**Requests for information you don't have:**
"I don't have that specific information available, but I can connect you with
someone who does. Would you like me to escalate this?"Voice Agent Considerations
When writing instructions for voice agents, consider the unique aspects of spoken conversation:
Adapt for Speech
## Voice-Specific Guidelines
- Keep responses concise—long answers are hard to follow when spoken
- Avoid lists longer than 3 items without confirmation
- Use verbal confirmation: "Got it", "I understand", "Let me check that"
- Spell out complex terms: "That's A as in Alpha, B as in Bravo"Handle Unclear Speech
## When Speech is Unclear
- If the transcription seems incomplete or garbled, politely ask the customer to repeat
- Example: "I didn't catch that clearly. Could you please repeat?"What Voice Agents Can and Cannot Detect
The agent receives transcribed text, not raw audio. This means:
- ✅ It can detect when transcriptions seem incomplete or unclear
- ❌ It cannot detect background noise, pauses, or tone of voice
Silence detection and timeout handling are configured in Call Configuration, not in instructions.
For more details on voice-specific considerations, see Voice vs Chat.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Too long | LLM may not follow all instructions | Prioritize and trim to essentials |
| Contradictory rules | Agent behaves unpredictably | Review for conflicts |
| No personality | Generic, robotic responses | Add character and tone guidelines |
| Missing boundaries | Agent does things it shouldn't | Explicitly define limitations |
| No examples | Agent interprets vaguely | Add concrete examples |
Related Documentation
- Profile - Set up agent identity and model
- Voice Settings - Configure voice characteristics
- Prompts for Agents - Advanced prompt engineering guide
