Profile
The Profile tab defines the administrative characteristics and language model for your Agent. These settings determine how your agent is identified in the platform and which AI model powers its responses.
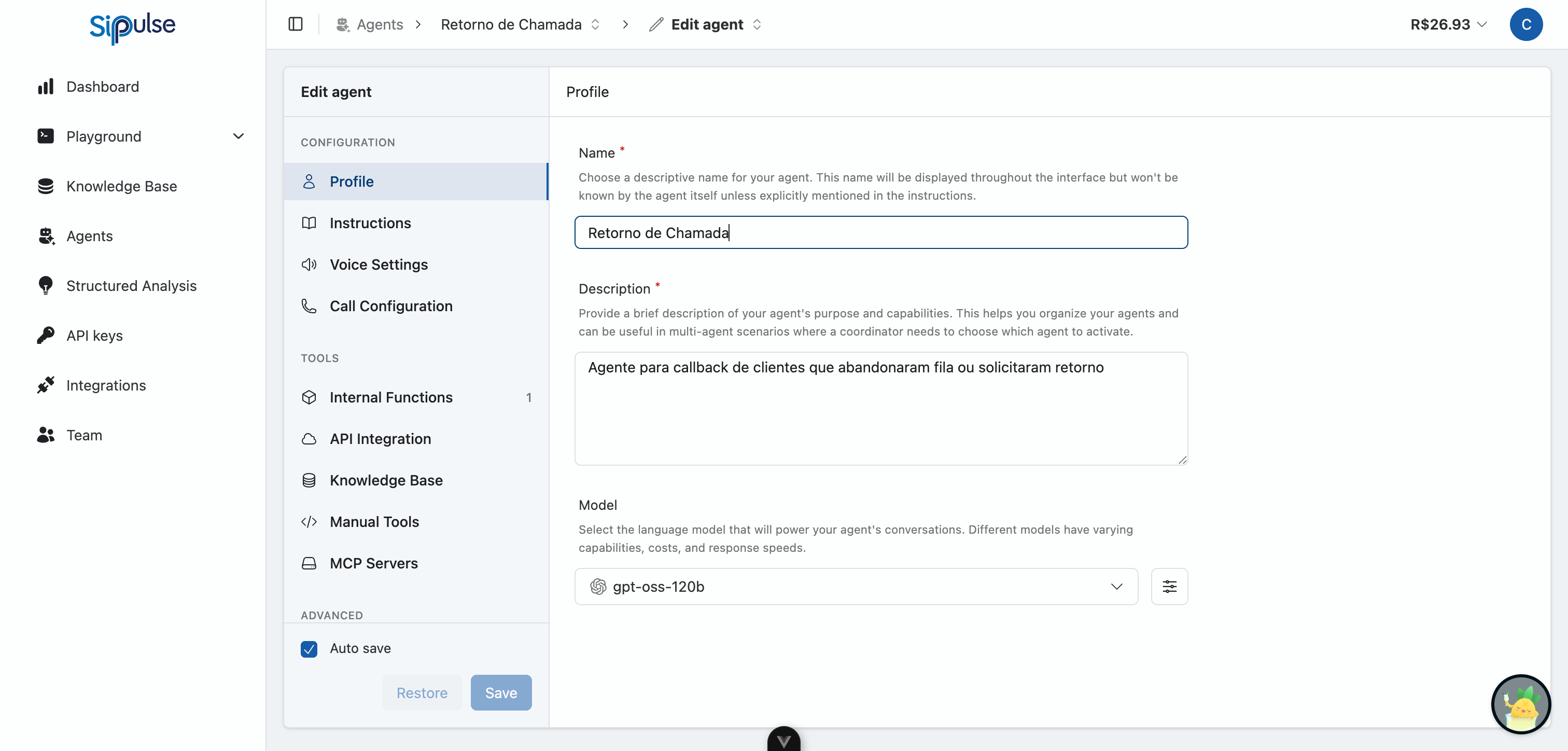
Name
Enter a unique and descriptive name for your agent. This name will be displayed throughout the interface and helps identify the agent on the platform.
Examples:
Customer Support - EnglishSales Qualifier - InboundTechnical Support Level 1
The Agent Doesn't Know Its Name
The agent itself is not aware of this name unless you explicitly include it in the instructions. If you want your agent to introduce itself as "Sarah", you need to write that in the instructions—the platform name is purely organizational.
Description
Provide a brief description of your agent's purpose and capabilities. While not visible to the agent itself, this description is valuable for:
- Documentation - Record the agent's intended use for team reference
- Team collaboration - Help team members quickly understand each agent's role
Good description example:
Handles first-tier customer support inquiries. Qualified to answer billing questions, reset passwords, and escalate technical issues to Level 2 support.
Model
Choose the AI model that will power your agent's conversations. Click the model dropdown to see available options from various providers.
Model Selection
The available models appear in the dropdown and vary over time as providers release new versions. Models generally fall into these categories:
| Category | Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Large/Flagship | Most capable, higher cost | Complex reasoning, nuanced conversations |
| Fast/Mini | Lower cost, faster response | High-volume, straightforward tasks |
| Specialized | Optimized for specific tasks | Varies by provider |
Choosing a Model
For most use cases, start with a fast model and upgrade to a larger one only if the agent struggles with complex reasoning. Voice agents especially benefit from faster models due to latency requirements.
Advanced Parameters
Click the Preferences button (gear icon) to configure advanced LLM parameters. The available parameters depend on the selected model—not all models support the same options.
Model-Specific Behavior
Parameters like Temperature and Top P behave differently across models. A temperature of 0.7 on one model may produce very different results on another. If you need precise control, consult the documentation for your specific model provider.
For most use cases, the default parameters work well. Only adjust if:
- Responses are too random or inconsistent (try lowering temperature)
- Responses are too repetitive (try increasing temperature)
- Responses are being cut off (increase max tokens if available)
Best Practices
Naming Conventions
Establish a consistent naming convention across your organization:
[Function] - [Channel/Language] - [Variant]
Examples:
- Support - Voice EN - Standard
- Support - Voice PT - After Hours
- Sales - Chat - Lead QualifierDescription Templates
Use a consistent template for descriptions:
[Primary function]. [Key capabilities]. [Limitations/escalation path].
Example:
Handles inbound sales inquiries for SaaS products. Can explain pricing,
schedule demos, and qualify leads. Transfers to human sales rep for
enterprise deals over $50k.Model Selection by Use Case
| Use Case | Recommended Model Type |
|---|---|
| Customer support (voice) | Fast models for lower latency |
| Complex sales qualification | Larger models for better reasoning |
| FAQ answering | Fast models with knowledge base |
| Technical troubleshooting | Larger models for complex problem-solving |
Related Documentation
- Instructions - Define your agent's behavior
- Voice Settings - Configure voice characteristics
- Testing Agents - Test your configuration
